Life
-
 Neuroscience
NeuroscienceElectrical brain implants may help patients with severe brain injuries
After deep brain stimulation, five patients with severe brain injuries improved their scores on a test of cognitive function.
-
 Animals
AnimalsFish beware: Bottlenosed dolphins may be able to pick up your heartbeat
Fish, sharks and platypuses are adept at sensing electrical signals living things give off. Bottlenosed dolphins make that list too, studies suggests.
-
 Animals
AnimalsThese nesting penguins nod off over 10,000 times a day, for seconds at a time
Micronaps net chinstrap penguins over 11 hours of sleep a day, offering some rest while staying vigilant against predators and competitors.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsThis bird hasn’t been seen in 38 years. Its song may help track it down
Using bioacoustics, South American scientists are eavesdropping on a forest in hopes of hearing the song of the long-missing purple-winged ground dove.
-
 Animals
AnimalsOne mountain in Brazil is home to a surprising number of these parasitic wasps
Darwin wasps were thought to prefer temperate areas. But researchers scoured a mountain in the Brazilian tropics and found nearly a hundred species.
-
 Life
LifeSome picky Australian mosquitoes may target frog nostrils for blood
The insects seem to sip from nowhere else on frogs’ bodies. Thinner skin or denser blood vessels near the nostrils might explain why.
By Jake Buehler -
 Animals
AnimalsThese bats are the only mammals known to mate more like birds
Male serotine bats have penises too large for penetration. To mate, the animals rub their genitals against each other, somewhat like birds’ cloacal kiss.
-
 Health & Medicine
Health & MedicineA brain-monitoring device may one day take the guesswork out of anesthesia
The automated device pairing brain activity and dosing kept two macaques sedated for 125 minutes, raising hopes of precision anesthesia for people.
-
 Animals
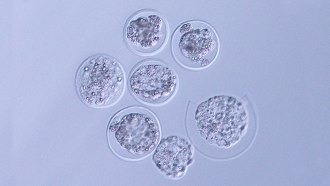
AnimalsThe first embryos from a mammal have now been grown in space
Mouse embryos in space can develop into clusters of cells called blastocysts. The result is a step toward understanding how human embryos will fare.
-
 Life
LifeCrabs left the sea not once, but several times, in their evolution
A new study is the most comprehensive analysis yet of the evolution of “true crabs.”
By Amanda Heidt -
 Chemistry
Chemistry‘Most Delicious Poison’ explores how toxins rule our world
In his debut book, Noah Whiteman tours through chemistry, evolution and world history to understand toxins and how we’ve come to use them.
-
 Life
LifeBonobos, like humans, cooperate with unrelated members of other groups
Cooperation between unrelated individuals in different groups without clear and immediate benefit was thought to be uniquely human. Its presence in bonobos may help explain its evolution.
By Jake Buehler